Annealing
ESPECIALLY FOR OUR USERS"Residual stresses generated during injection molding can significantly impact the mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and long-term stability of plastic parts. Annealing, a controlled heat treatment process, enables the relaxation of these stresses and promotes improved crystallinity and material uniformity. Annealing is a post-processing step used to reduce these stresses, improve part strength, and enhance dimensional stability. It involves heating molded parts to a controlled temperature and then cooling them slowly. To optimize efficiently this process, Moldex3D can be used to predict how annealing affects stress, shrinkage, and warpage, allowing users to improve product quality without extensive physical testing.
Annealing is used to reduce inherent stresses that may be introduced during the molding and cooling processes.
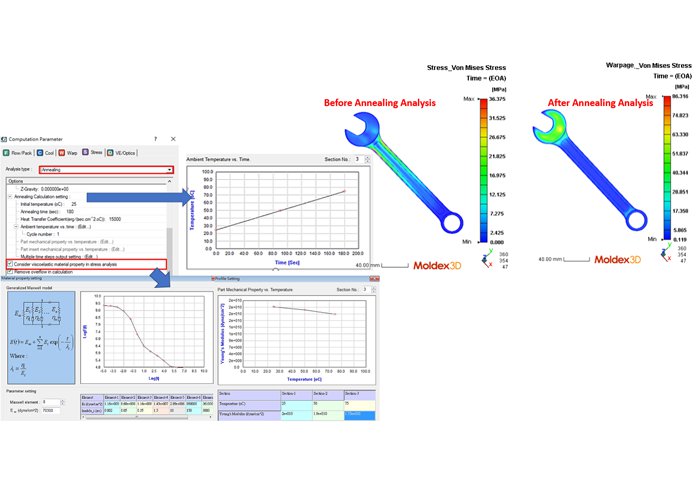
With the Moldex3D Stress module, annealing analysis can be performed to monitor the behavior of the products under a varied ambient temperature environment. Annealing analysis should consider the flow and thermal induced strain and stress during filling, cooling and warpage stage, so the corresponding analysis sequences should be process before summit annealing analysis.
To perform an annealing simulation in Moldex3D, user need to first set up the injection molding simulation by defining part geometry, material properties, and molding parameters like filling, cooling, and warpage. Then, the initial analysis can be launched to gather data for the annealing process. For the Annealing calculation, the Stress module must be enabled in the warpage calculation parameters, and users can select either linear or viscoelastic annealing computation based on the material model. Then, it is also possible to configure the boundary conditions, including part and mold temperatures, heating and cooling rates, and ambient conditions. For the linear Annealing computation, users should input temperature-dependent material properties, and for Viscoelastic Annealing, define time-dependent behaviour in Tab setting. Finally, execute the simulation to analyze temperature distribution, residual stresses, deformation, and material behavior during the heating, packing, and cooling phases.
After running the simulation, users analyze the results, including displacement, Von Mises stress, shear stress, and temperature distribution, to evaluate the part's performance and stability. Based on these results, optimize the annealing process by adjusting parameters such as temperature and cooling rate to achieve better dimensional stability and stress relaxation.