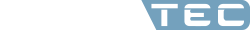
Determining the Optimal Product Geometric Design in the Shortest Time
ESPECIALLY FOR OUR USERSA general plastic product manufacturing process involves many stages including product and structure designs, mould designs, mould tooling and injection moulding. If the part design is not appropriate enough, it will cause difficulties for the production in later stages or more communication effort on the design changes and fixing of the part and mold. During the plastic product design stage, analysing the Moldex3D simulation to approach the optimal designs will prevent potential problems and ensure a smooth mass production.
There are usually Design for Manufacturing (DFM) inspections in the product design stage. Common DFM point to be reviewed are e.g. the shrinkage values of plastic materials, draft angles and whether there are barbs or not. An additional and important are the part thickness, rib, and boss designs as well. These inspections can be completed through CAD features or manual inspection drawings. For instance, although we normally look for a uniform part thickness, when thickness variations are required, it suggest designs as schematically shown in figure (left). On the other hand, the figure also show the suggested designs of ribs, and boss designs. However, plastic injection moulding is a dynamic process and same plastic material grade made by different manufacturers and with different models can make big differences in material characteristics. In addition, different injection machines have different machine responses, and different engineering conditions will affect product qualities. As the result, the problems still occur in actual manufacturing even with DFM. For example, although we have followed the thickness and rib design suggestions, the final products can still have excessive warpage, low structural strength. The surface defects or even incomplete filling can be the result and production will not be able to manufacture it.
As such, there are no correct rules exactly for all product designs. Apart from using CAD software to proceed DFM inspections, analyses of CAE simulations can further assist to adjust the geometric dimensions, validate the optimized designs, and troubleshoot the issues iteratively. Such iterative design changes and validations are a long-winded process and to master this challenge, Moldex3D tool chain (e.g. Studio, SYNC …) from 2021 supports the geometry optimization tools, helping users greatly simplify the CAE analysis workflow. With this tool chain, the designs with all the dimension variations and the corresponding CAE analysis results can be completed through several simple steps.
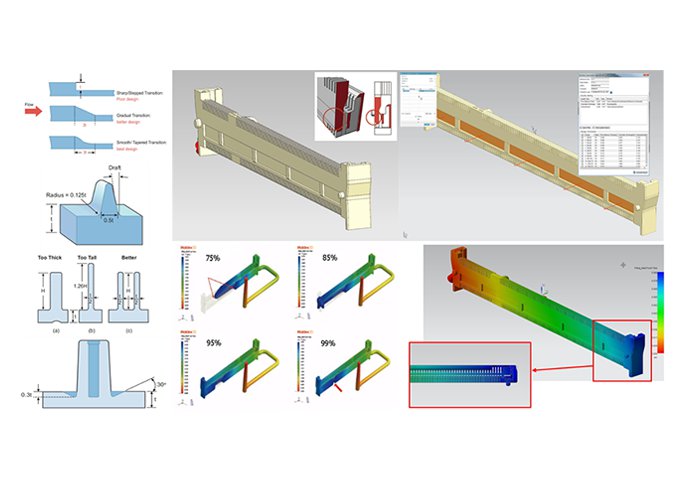
The case of a connector shown in the figure (right) demonstrates how to utilize Moldex3D SYNC as an example to attain the optimized geometric designs. The figure shows the original product model that has passed the DFM inspection and its initial simulation result. As shown in the flow analysis, flow imbalance occurs at both sides of the connector. It also shows the warpage analysis result that would cause a problem for the pin header when it is being inserted, which must be improved before manufacturing. From the cross-section of the original design, both sides have different thickness, and the thicker end needs to be slightly modified. Although it shows that changing the thickness can improve the flow imbalance and warpage, (structural analysis is also required), the designer cannot determine how much modification is needed to achieve the optimal thickness and it will be very time-consuming to analyse every design with different thickness. With the geometry optimization tool in Moldex3D SYNC, the user will quickly specify the variated parameters and set all the analysis groups and thus attain a set of optimal analysis results in which the warpage has been improved while the melt front almost coincides at the end.
Would you like to know more?
Please contact us: + 49 (0)241-565 276-0 or send us an email to info@simpatec.com .